Hey Database gurus, I've started deep diving into the Open source databases - Oracle MySQL database, Read through the official MySQL documentation for MySQL 8.4 and 9.3 (as of April 2025) still lists mysqladmin as a supported client for administrative operations such as checking server status, creating and dropping databases, and shutting down the server..
 |
| The mysqladmin command sub-commands and scope |
Prerequisite: Install MySQL on Ubuntu on Killercoda
Login to your https://killercoda.com/ account select the Ubuntu latest playground terminal run the installation commands as given below:
Install MySQL server
apt install -y mysql-server
mysql version
Top 'mysqladmin' command for monitoring examples
Here are some common mysqladmin command examples for administering a MySQL/MariaDB server:
We are running mysqladmin command on the same MySQL/MariaDB server then default 'root' will be the admin user and without password it will work for the sub-command.
---
1. Connect to MySQL Server
mysqladmin -u [username] -p version
mysqladmin version
- This command to check the MySQL server connectivity, when we use -p option it will prompts for the password and displays the server version.
Example for the version:
 |
| The mysqladmin command with version subcommand |
2. Check MySQL Server Status
The subcommand 'status' will work as follows:
mysqladmin -u root -p status
- Shows server status that includes (uptime, threads, queries, etc.). This will be used as MySQL/MariaDB monitoring command.
Example for the status:
 |
| mysqladmin stat command output |
3. Create a Database
mysqladmin -u root -p create [database_name]
mysqladmin create database_name
- This 'create' subcommand helps you to creates a new database with the name you provided as argument database_name.
Example for the create:
 |
| create a database using mysqladmin |
4. Drop a Database
mysqladmin -u root -p drop [database_name]
- This is critical subcommand use it rethink about it in realtime project, because it will deletes a database that you provide as database_name (confirmation required).
 |
| Drop a database using mysqladmin |
5. Change Root Password
mysqladmin -u root -p password "new_password"
- This is not really secure way if you provide the new password in the commandline. Changes the root user's password (replace new_password).
---
6. Check Active Processes
mysqladmin -u root -p processlist
- This is another important troubleshooting/monitoring command, which will lists all active database connections/threads.
 |
| process list of mysql server |
7. Kill a Process
mysqladmin -u root -p kill [process_id]
- This is purely troubleshoot command, when CPU load spikes up you can smartly execute this command by referring to the proc command output from there identify the process/thread that is causing load on the server. Terminates a specific thread (use processlist to find the ID).
---
8. Shut Down the Server
mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown
mysqladmin shutdown
- Stops the MySQL server gracefully. This can be used when you work on weekly maintainance or during MySQL server patching we may use this.
 |
| MySQL server shutdown using mysqladmin |
9. Flush Commands
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-hosts # Flush host cache
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-logs # Flush logs
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-privileges # Reload privileges (same as `reload`)
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-tables # Flush all tables
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-status # Reset status variables
When you observed memory related spikes on the MySQL Server, we need to analyse and run the flush commands at different levels. choose the option smartly and execute them.
---
10. Check Server Variables
mysqladmin -u root -p variables
- Displays all server configuration variables.
Better to use what all impacting variables you wish to filter out using the Linux command `grep` as a combination with this variables subcommand.
Example for variables:
mysqladmin variables |grep conn
mysqladmin extended-status |grep Ssl_
mysqladmin variables |grep max_connection
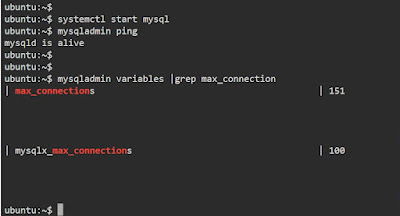 |
| mysqladmin variables filtered with grep |
Useful to compare settings in different environments (e.g., DEVDB vs QADB or DEVDB vs PREPRODDB).
Helpful when tuning performance of the MySQL server with variables such as (e.g., innodb_buffer_pool_size, query_cache_size, etc.).
11. Ping the Server
mysqladmin -u root -p ping
- Checks if the server is running. It is just like Linux ping command to find the server reachable.
---
12. Extended Status
mysqladmin -u root -p extended-status
- This is also monitoring command to deep dive, It shows detailed server status metrics.
---
13. Remote Server Connection
mysqladmin -h [hostname/IP] -P [port] -u [user] -p [command]
Here we need to supply the inputs of remote server details hostname, port, user
mysqladmin -h 192.168.1.100 -P 3306 -u root -p status
14. Using Configuration Files
mysqladmin --defaults-file=/path/to/my.cnf [command]
- Useful for servers with custom configurations.
---
Notes:
- Replace [username], [database_name], etc., with actual values.
- Avoid including passwords directly in commands (use -p to prompt securely).
- For older MySQL versions, some commands (e.g., password) may differ.
---
Troubleshooting Tips
- Connection Issues : Use -h [host], -P [port], or --protocol=tcp if connecting remotely.
- Permission Issues : Ensure the user has admin privileges (e.g., GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES).
- Short cuts for subcommands can be used status - stat, processlist - proc
- combine multiple subcommands to get more monitoring outcomes together using stat proc ping in single line.
mysqladmin stat
mysqladmin proc
mysqladmin proc stat
mysqladmin stat ping proc
 |
| The mysqladmin for monitoring with multiple sub-commands |
Hope you enjoyed this hands-on Realtime monitoring and troubleshooting tips for MySQL/MariaDB server. Write your takeaway from this post in the comment box.










Comments
Post a Comment